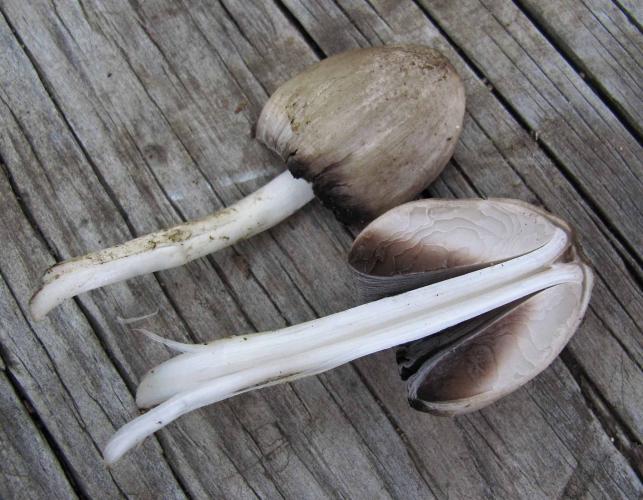
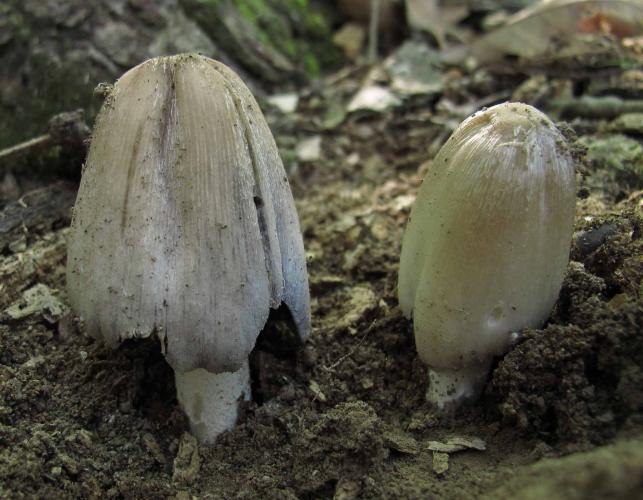
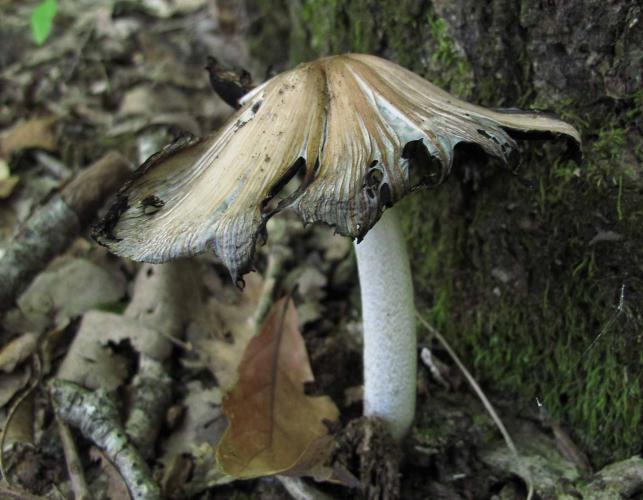
Gray-brown, bell-shaped, radially lined cap; inky gills. Grows in clusters on the ground, usually near rotting or buried wood. May–September. Cap egg-shaped, becoming bell-shaped; gray to gray-brown; texture dry, smooth, silky, with minute scale remnants; faintly radially lined; with age, cap and gills become inky and liquefy. Gills broad; spacing crowded; white, becoming lavender-gray, then blackish and inky; attachment free. Stalk with equal sides or slightly enlarged toward the base; white; texture dry, silky, fibrous; hollow. Spore print black. Spores magnified are elliptical, smooth, with pore at tip.
Lookalikes: The mica cap (Coprinellus micaceus) has a tawny brown cap.
Cap width: 1½–3 inches; stalk length: 3–6 inches; stalk width: ¼–1 inch.
Statewide.
Habitat and Conservation
Grows in clusters on the ground, usually near rotting or buried wood.
Status
A good edible, but with caution: If you drink any alcoholic beverage within 3 days before or after eating this mushroom, you can become very sick, with body tingling, heart palpitations, headache, and nausea. Otherwise, it is a good edible. Because of the trouble it has caused for hearty drinkers, it is sometimes called "tippler's bane."
Life Cycle
Mushrooms exist most of the time underground or within rotting logs as a network of cells (mycelium) connected to the materials they digest, in this case, rotting wood. When ready to reproduce, the mycelium develops the mushroom, which is a reproductive structure. Spores are produced in the gills and are released to begin new mycelia elsewhere. In inky caps, the spores are distributed when the cap liquefies.
Human Connections
When you are eating any wild mushroom for the first time, even one that is supposed to be edible, it is a good idea to sample only a small amount at first, since some people are simply allergic to certain chemicals in certain fungi. Make sure they are cooked, too.
Ecosystem Connections
This is one of the many fungus species that live on decaying wood. It and other saprobic fungi play an incredibly important role in breaking down the tough materials wood is made of and returning those nutrients to the soil.






Mushrooms are a lot like plants, but they lack chlorophyll and have to take nutrients from other materials. Mushrooms are neither plants nor animals. They are in a different kingdom — the fungi. Fungi include the familiar mushroom-forming species, plus the yeasts, molds, smuts, and rusts.
Always be cautious when eating edible mushrooms. Be absolutely sure of the ID, and only eat a small amount the first time you try it to avoid a reaction..





















