Trees, Shrubs and Woody Vines
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rhus glabra
Description
Colonies of smooth sumac are most noticeable in early autumn, because the leaves turn brilliant red! You can make drinks and jellies from the clusters of fuzzy red berries.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rhus aromatica
Description
Unlike its cousin poison ivy, fragrant sumac is a peasant, nontoxic plant. Note the middle leaflet of its "leaves of three": On fragrant sumac, there is no (or at most a very short) leaf stalk on that middle leaflet. Also, fragrant sumac has hairy, reddish fruits (not waxy whitish ones).
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rhus copallinum
Description
Winged sumac is most common south of the Missouri River. The "wings" in the name refer to the narrow, flattened leafy structures running along the central stems of the compound leaves.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rhus spp.
Description
Sumacs are shrubs or small trees that often form colonies from their creeping, branched roots. The foliage usually turns brilliant shades of red in early autumn. The clusters of berrylike fruits are red.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Staphylea trifolia
Description
American bladdernut is a thicket-forming shrub or small tree that grows in moist soils. It produces clusters of bell-shaped white flowers in spring and unusual 3-parted air-filled capsules in late summer that turn papery and persist into winter.
Media
Species Types
Scientific Name
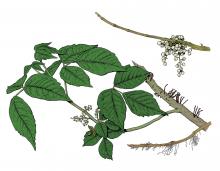
Toxicodendron radicans
Description
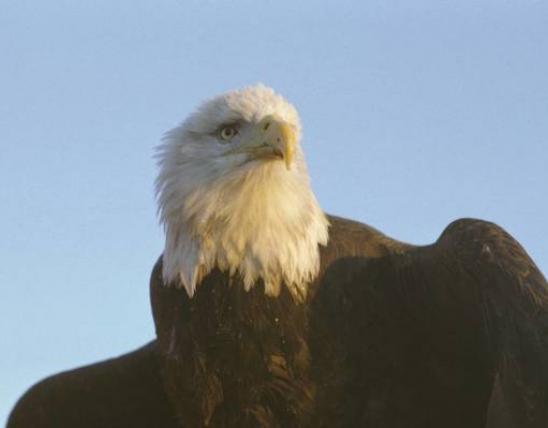
Poison ivy is a toxic plant that contains an oil in all its parts that, if you come into contact with it, can cause an intense skin reaction. Learn to recognize it, and sidestep it on your outings.
Media
Species Types
Scientific Name
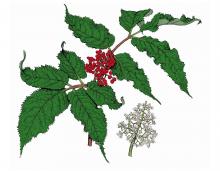
Sambucus pubens
Description
Red-berried elderberry reaches 24 feet in height and does not form colonies. Its white flowers, and later, red berries, are in pyramidal clusters. In Missouri, it’s known only from Marion County.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rosa multiflora
Description
Starting more than a century ago, this nonnative rose was planted across America — for many good reasons — but multiflora rose has proven to be invasive, and now the goal is to stop its spread.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rosa setigera
Description
Also called climbing rose, prairie rose is most common near woodlands, where it climbs and trails on neighboring shrubs and small trees.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rubus occidentalis
Description
Black raspberries resemble blackberries, but when ripe, the fruits fall away as a caplike unit from the receptacle. Leaflets appear white underneath. The canes are whitish-coated when young; they arch down and take root at the tips. Native and scattered statewide.
See Also
About Trees, Shrubs and Woody Vines in Missouri
There are no sharp dividing lines between trees, shrubs, and woody vines, or even between woody and nonwoody plants. “Wood” is a type of tissue made of cellulose and lignin that many plants develop as they mature — whether they are “woody” or not. Trees are woody plants over 13 feet tall with a single trunk. Shrubs are less than 13 feet tall, with multiple stems. Vines require support or else sprawl over the ground.





















