Trees, Shrubs and Woody Vines
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Gleditsia triacanthos
Description
Though it doesn’t reach a stately size, honey locust commands respect for its many large, strong, usually branched thorns, which can puncture tractor tires as easily as they can poke through tennis shoes! The long, leathery, twisting pods are relished by cattle and by wildlife.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Juglans nigra
Description
Easily Missouri’s most valuable tree, the black walnut provides the finest wood in the world, as well as delicious nuts. Both are in high demand and thus form an important part of Missouri’s economy.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rhus glabra
Description
Colonies of smooth sumac are most noticeable in early autumn, because the leaves turn brilliant red! You can make drinks and jellies from the clusters of fuzzy red berries.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Carya texana
Description
Black hickory's nut, like that of the pignut hickory, is awfully hard to crack. Because rural Ozarkers noticed their hogs had no trouble extracting the sweet kernels, both species came to be called "pignut hickories."
Media
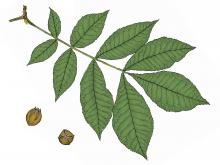
Species Types
Scientific Name
Carya cordiformis
Description
Of the several hickories in Missouri, bitternut hickory is the only one with long, bright yellow buds. Its common name refers to the bitter taste of the nut — but the flavor doesn't put off squirrels, mice, and deer!
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Carya illinoinensis
Description
The pecan, a type of hickory, is one of Missouri’s favorite nut trees. Originally pecan had a fairly limited, southern distribution, but today it is found in and out of cultivation nearly statewide, owing to the popularity of the nuts.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Rhus aromatica
Description
Unlike its cousin poison ivy, fragrant sumac is a peasant, nontoxic plant. Note the middle leaflet of its "leaves of three": On fragrant sumac, there is no (or at most a very short) leaf stalk on that middle leaflet. Also, fragrant sumac has hairy, reddish fruits (not waxy whitish ones).
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Various species in the genus Crataegus
Description
Our state flower, the hawthorn, is solidly represented in Missouri. There are about 100 different kinds of hawthorns that occupy almost every kind of soil in every part of the state. These members of the rose family are closely related to apples.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Ilex decidua
Description
Possum haw, or deciduous holly, is the more common of two native Missouri hollies that lose their leaves each fall. This shrub or small tree is eye-catching in the fall and winter with its bright red berries.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Prunus americana
Description
A shrub or small tree with clusters of white flowers in the spring, and small, edible, red or yellow fruits in mid- to late summer, wild plum is a popular tree for landscaping.
See Also
About Trees, Shrubs and Woody Vines in Missouri
There are no sharp dividing lines between trees, shrubs, and woody vines, or even between woody and nonwoody plants. “Wood” is a type of tissue made of cellulose and lignin that many plants develop as they mature — whether they are “woody” or not. Trees are woody plants over 13 feet tall with a single trunk. Shrubs are less than 13 feet tall, with multiple stems. Vines require support or else sprawl over the ground.





















